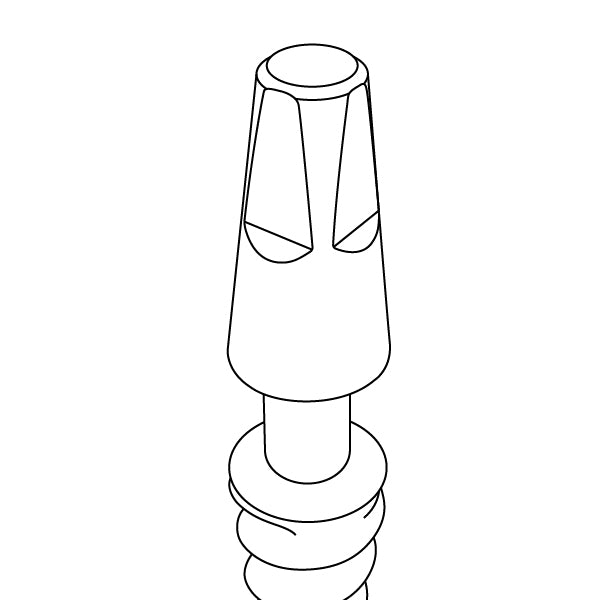
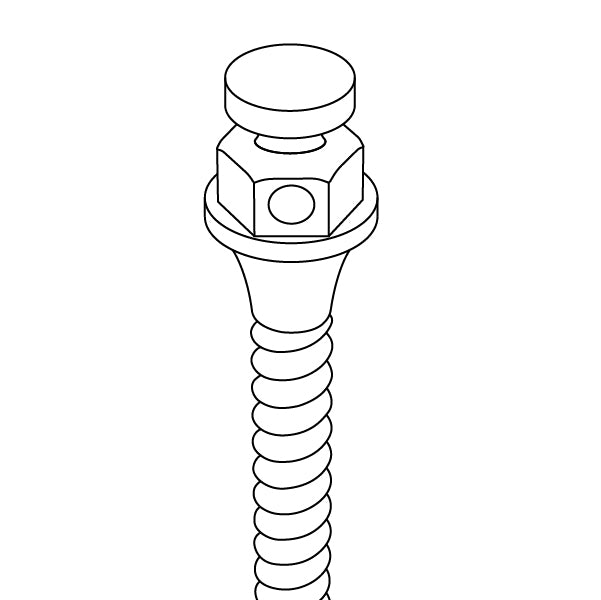
Our Internal Hex Connection is a widely trusted and extensively used solution in dental implantology. This connection type features a six-sided, hexagonal shape within the implant, creating a secure interlocking mechanism. This hexagonal design is essential for preventing rotational movements, ensuring that the abutment stays firmly in place. The precise hexagon angles evenly distribute forces, reducing stress on the implant and surrounding bone.
GDT Implants offer versatile solutions for any clinical case. Our implants come in a variety of types, shapes, and surface treatments to cater to diverse needs. Choose GDT Internal Hex Connection for durable, reliable, and secure dental implants that offer superior performance and patient satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions About INTERNAL HEX IMPLANTS
The anatomical and clinical needs of patients vary from one individual to another. It’s important for dental clinicians to have a range of products at their disposal, allowing them to tailor treatments to each patient's specific requirements and ensure the highest quality of care.
At GDT Dental Implants, we offer a comprehensive range of solutions that address the needs of clinicians and clinics worldwide. Since the anatomical and clinical needs of patients vary, we provide multiple implant design options to choose from.
Choosing the right internal hex implant for dental procedures is crucial. Our designs cater to different bone densities, aesthetic requirements, and chewing force distributions, ensuring the best outcome for every patient.
GDT Dental Implants ensure that our products are up to date with the latest safety standards. By integrating our implants with different surface treatments and navigating regulatory changes, we offer a wide range of options, allowing you to provide personalized and effective dental treatments.
Most research papers that have studied participants over a 10-year period have shown positive success rates (about 90% to 95%) of internal hex implants. This can be attributed to the implant’s design, which ensures exceptional mechanical stability while reducing micro-movements at the implant-abutment interface.
While some clinicians might have concerns over the safety of internal hex implants, our manufacturing processes prioritize premium-quality dental products that are exceptionally precise.
At GDT Dental Implants, our internal hex implants are made from high-grade titanium, known for its corrosion resistance and biocompatibility properties. They are incredibly durable and aid in effective osseointegration.
Our stringent manufacturing processes, including surface modifications like sandblasting and acid etching, ensure that our internal hex implants have incredibly high success rates.
Besides premium-quality dental products, good clinical practice, proper patient maintenance, and correct placement techniques play a crucial role in achieving a higher success rate with internal hex implants.
At GDT Dental Implants, our internal hex implants are made from titanium grade 5 (TI-6AL-4V ELI), a material highly favored in dentistry for its incredible strength, durability, and biocompatibility.
Titanium is an excellent choice for internal hex implants as it supports effective osseointegration, encouraging bone growth into the dental fixture and ensuring a stable foundation.
We offer two treatment options at GDT Dental Implants: RBM and SLA. Both of these treatments enhance the performance of the implant by increasing bone-to-implant contact, which can accelerate the healing process.
The key differences between sandblasted, large-grit, acid-etched (SLA) and resorbable blast media (RBM) surface treatments are as follows:
- SLA involves sandblasting the implant with large grit particles followed by acid etching. This creates a micro-rough surface that enhances bone cell attachment and promotes rapid osseointegration.
- RBM uses a biocompatible, resorbable material like calcium phosphate to blast the implant. This process produces a moderately rough surface that not only aids bone integration but also enhances bioactivity by releasing beneficial ions that stimulate bone growth.
It’s important to understand that while both treatments aim to improve bone-to-implant contact and aid in osseointegration, they address different clinical needs based on the desired balance of mechanical stability and biological interaction.
Recently viewed